Prevalence
The number of cases that exist in a given population
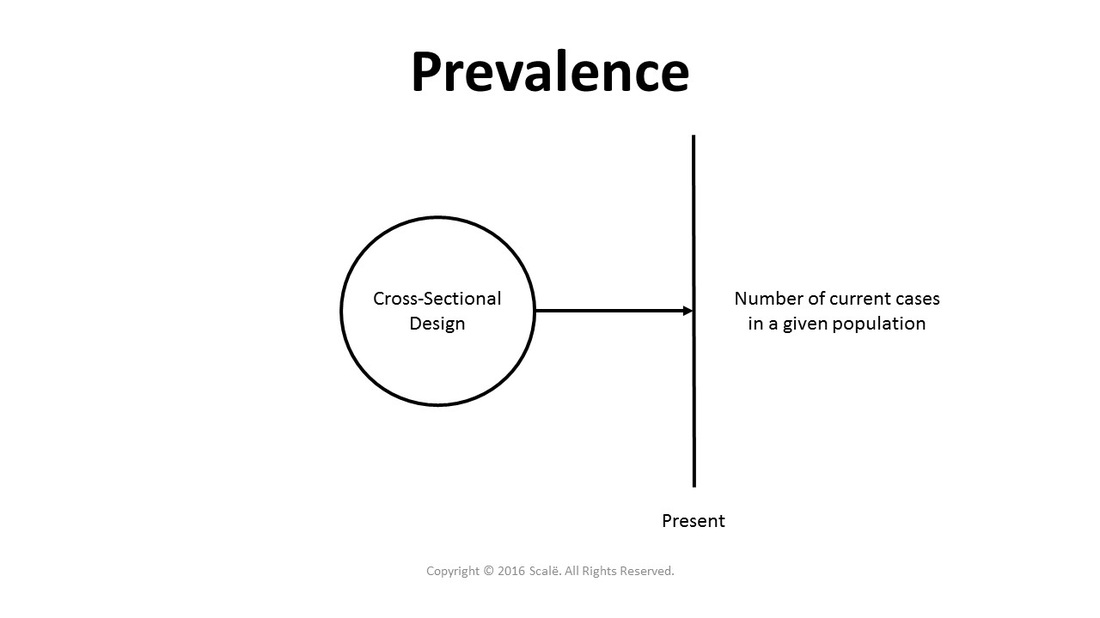
Prevalence is defined as the number of current cases in a given population. Prevalence is a retrospective measure because it is generated using a cross-sectional design. The odds ratio with 95% confidence interval is used as a measure of association and is closely tied to comparing prevalence between sub-groups and sub-populations. Although the two terms are at times used interchangeably, prevalence is different from incidence because it is established in retrospective designs, while incidence is calculated in prospective studies.
When calculating prevalence, the scale of measurement of the outcome dictates what statistic is used. If the outcome is categorical, then frequency statistics are used to establish the percentage (%) of the sample (population) that possesses the outcome of interest. With ordinal outcomes, researchers report medians and interquartile ranges as a measure of prevalence. Finally, for continuous outcomes, means and standard deviations are used to describe prevalence.
When calculating prevalence, the scale of measurement of the outcome dictates what statistic is used. If the outcome is categorical, then frequency statistics are used to establish the percentage (%) of the sample (population) that possesses the outcome of interest. With ordinal outcomes, researchers report medians and interquartile ranges as a measure of prevalence. Finally, for continuous outcomes, means and standard deviations are used to describe prevalence.
Click on the Relative Risk button to continue.
Statistician For Hire
DO YOU NEED TO HIRE A STATISTICIAN?
Eric Heidel, Ph.D. will provide statistical consulting for your research study at $100/hour. Secure checkout is available with PayPal, Stripe, Venmo, and Zelle.
- Statistical Analysis
- Sample Size Calculations
- Diagnostic Testing and Epidemiological Calculations
- Psychometrics