Odds ratio with 95% confidence interval
The width and direction of the confidence interval is the primary inference with an odds ratio
The odds ratio with 95% confidence interval is the inferential statistic used in retrospective case-control designs, chi-square analyses (unadjusted odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals), and in multivariate models predicting for categorical, ordinal, and time-to-event outcomes. The width of the confidence interval of the odds ratio is the inference related to the precision of the treatment effect.
If the confidence interval of an odds ratio crosses over 1.0, then researchers have a non-significant association between the variables.
If the odds ratio and confidence interval are both entirely above 1.0, then the outcome is MORE LIKELY to occur as a result of the treatment or exposure.
If the odds ratio and confidence interval are both entirely below 1.0, then the outcome is LESS LIKELY to occur as a result of treatment or exposure, denoting a "protective" effect.
If the confidence interval of an odds ratio crosses over 1.0, then researchers have a non-significant association between the variables.
If the odds ratio and confidence interval are both entirely above 1.0, then the outcome is MORE LIKELY to occur as a result of the treatment or exposure.
If the odds ratio and confidence interval are both entirely below 1.0, then the outcome is LESS LIKELY to occur as a result of treatment or exposure, denoting a "protective" effect.
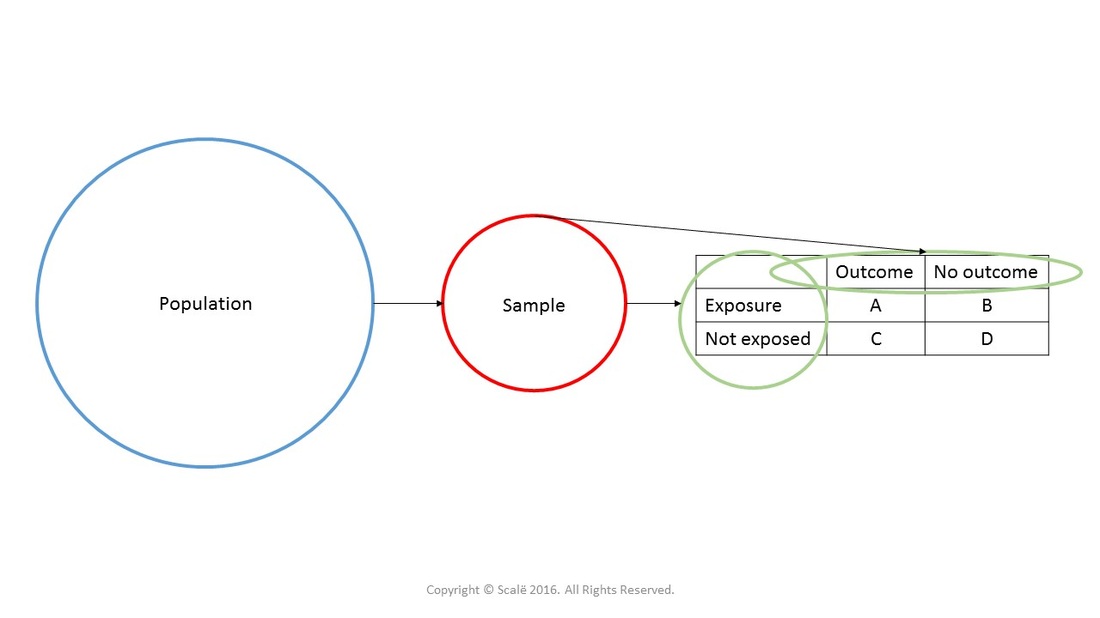
The research design of an odds ratio is set up like below.
Research Design and the 2x2 table
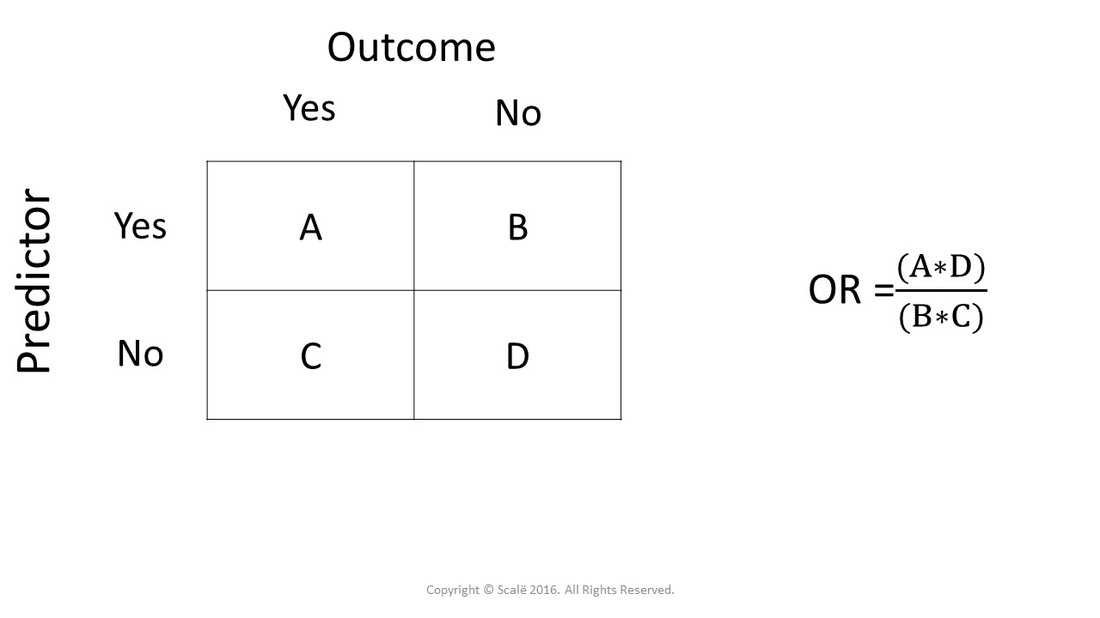
When researchers use a retrospective case-control design, the odds ratio with 95% confidence interval is used as the primary inference. In the table below, one can see that the formula is (A*D) / (B*C).
Odds Ratio Calculation
Confidence intervals of odds ratios and sample size
The width of the confidence interval associated with an odds ratio is the inference. Due to measurement error in categorical variables, a 95% confidence interval has to be wrapped around the odds ratio to understand where the true treatment effect may exist. Narrower confidence intervals allow for more precision of the treatment effect. Wider confidence intervals decrease precision meaning that the true treatment effect may lie anywhere across a wide continuum.
Click on the Prevalence button to continue. Click on the Download Database button for a database structured for odds ratio data.
Hire A Statistician
DO YOU NEED TO HIRE A STATISTICIAN?
Eric Heidel, Ph.D., PStat will provide you with statistical consultation services for your research project at $100/hour. Secure checkout is available with Stripe, Venmo, Zelle, or PayPal.
- Statistical Analysis on any kind of project
- Dissertation and Thesis Projects
- DNP Capstone Projects
- Clinical Trials
- Analysis of Survey Data