Appraising systematic review evidence
Assess methodological rigor, publication bias, and pooled effects
A systematic review (SR) is an aggregated analysis of existing studies that yields an overall measure of effect. Systematic reviews are considered the highest level of applied clinical evidence. When appraising a systematic review, there are certain criteria that have to be met in regards to heterogeneity of effect, publication bias, and methodological rigor.
Appraisal criteria for systematic review evidence
After reading the systematic review, ask these questions:
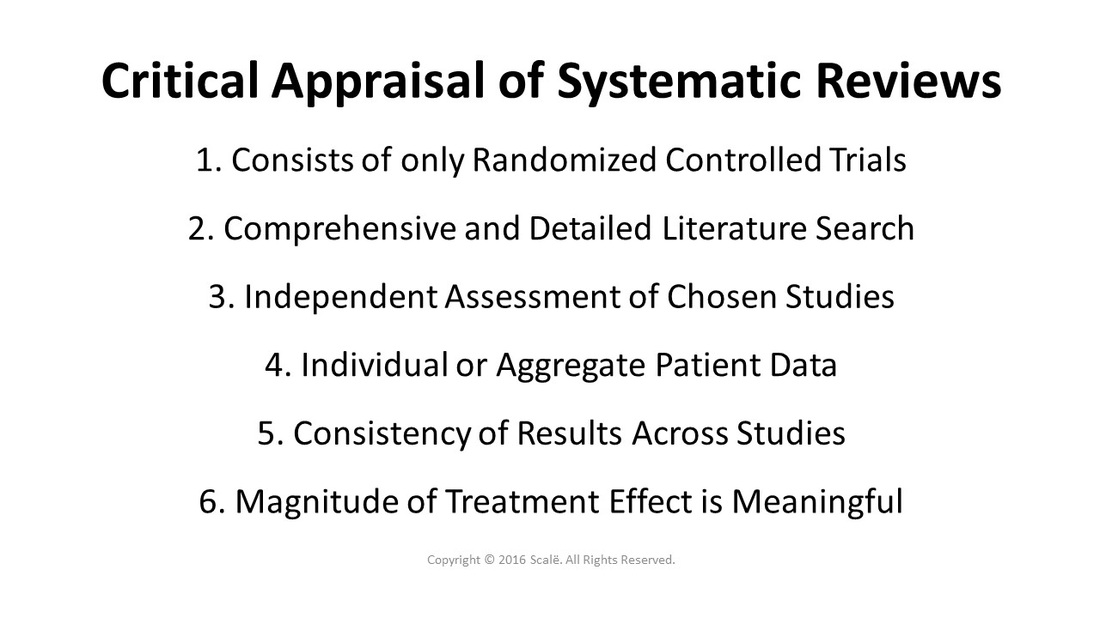
1. Did the systematic review contain only randomized trials?
2. Was a comprehensive and detailed literature search conducted for relevant trials?
3. Were the individual studies assessed for validity by independent raters?
4. Was individual or aggregate patient data used for the analysis?
5. Are the results consistent across studies?
6. Is the magnitude of the treatment effect clinically meaningful in the current clinical situation?
1. Did the systematic review contain only randomized trials?
2. Was a comprehensive and detailed literature search conducted for relevant trials?
3. Were the individual studies assessed for validity by independent raters?
4. Was individual or aggregate patient data used for the analysis?
5. Are the results consistent across studies?
6. Is the magnitude of the treatment effect clinically meaningful in the current clinical situation?
Click on the Applying SR Evidence button to continue.
Hire A Statistician
DO YOU NEED TO HIRE A STATISTICIAN?
Eric Heidel, Ph.D., PStat will provide you with statistical consultation services for your research project at $100/hour. Secure checkout is available with Stripe, Venmo, Zelle, or PayPal.
- Statistical Analysis on any kind of project
- Dissertation and Thesis Projects
- DNP Capstone Projects
- Clinical Trials
- Analysis of Survey Data