Repeated-measures t-test
Compare two observations of a continuous outcome after meeting statistical assumptions
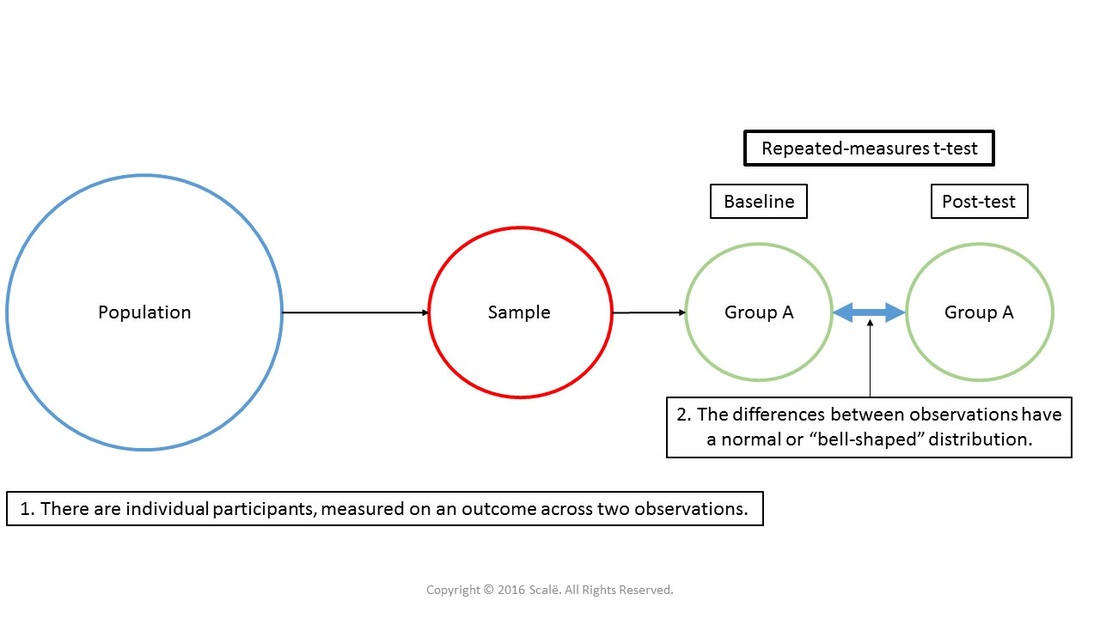
The repeated-measures t-test, also known as the paired samples t-test, is used to assess the change in a continuous outcome across time or within-subjects across two observations. There is only one group of participants with a repeated-measures t-test and their baseline or "pretest" mean and standard deviation serves as a control that is compared to their second or "posttest" mean and standard deviation. Repeated-measures t-tests can also compare "within-subjects" observations of an outcome, being within the same entity or unit of measurement.
The figure below depicts the use of a repeated measures t-test. There is only one group being observed at two within-subjects observations or two time points for a continuous outcome. The assumption of normality of difference scores has been met. A repeated-measures t-test is used to assess the change in a continuous outcome at two within-subjects observations or two time points.
The steps for conducting a repeated-measures t-test in SPSS
1. The data is entered in a within-subjects fashion.
2. Click Analyze.
3. Drag the cursor over the Compare Means drop-down menu.
4. Click on Paired-Samples T Test.
5. Click on the first observation of the continuous outcome.
7. Click on the arrow button to move the first observation of the outcome variable into the Test Pairs box under the Variable1 column.
8. Click on the second observation of the continuous outcome.
9. Click on the arrow button to move the second observation of the outcome variable into the Test Pairs box under the Variable2 column.
10. Click OK.
2. Click Analyze.
3. Drag the cursor over the Compare Means drop-down menu.
4. Click on Paired-Samples T Test.
5. Click on the first observation of the continuous outcome.
7. Click on the arrow button to move the first observation of the outcome variable into the Test Pairs box under the Variable1 column.
8. Click on the second observation of the continuous outcome.
9. Click on the arrow button to move the second observation of the outcome variable into the Test Pairs box under the Variable2 column.
10. Click OK.
The steps for interpreting the SPSS output for a repeated-measure t-test
1. In the Paired Samples Statistics table, there are several important pieces of information about each observation of the continuous outcome including the size of each observation (N) and their respective means (Mean) and standard deviations (Std. Deviation). Disregard the Std. Error Mean values for practical purposes.
2. In the Paired Samples Test table, look at the p-value associated with Sig. (2-tailed) column. This is the p-value that is interpreted.
If it is LESS THAN .05, then researchers have evidence of a statistically significant difference in the continuous outcome across time or within-subjects.
If the p-value is MORE THAN .05, then researchers have evidence that there is NOT a statistically significant difference in the continuous outcome across time or within-subjects.
2. In the Paired Samples Test table, look at the p-value associated with Sig. (2-tailed) column. This is the p-value that is interpreted.
If it is LESS THAN .05, then researchers have evidence of a statistically significant difference in the continuous outcome across time or within-subjects.
If the p-value is MORE THAN .05, then researchers have evidence that there is NOT a statistically significant difference in the continuous outcome across time or within-subjects.
Click on the Download Database and Download Data Dictionary buttons for a configured database and data dictionary for repeated-measures t-test. Click on the Adjusting for Multiple Comparisons button to learn more about Bonferroni, Tukey's HSD, and Schefee's test. Click on the Validation of Statistical Findings button to learn more about bootstrap, split-group, and jack-knife validation methods.
Hire A Statistician
DO YOU NEED TO HIRE A STATISTICIAN?
Eric Heidel, Ph.D., PStat will provide you with statistical consultation services for your research project at $100/hour. Secure checkout is available with Stripe, Venmo, Zelle, or PayPal.
- Statistical Analysis on any kind of project
- Dissertation and Thesis Projects
- DNP Capstone Projects
- Clinical Trials
- Analysis of Survey Data