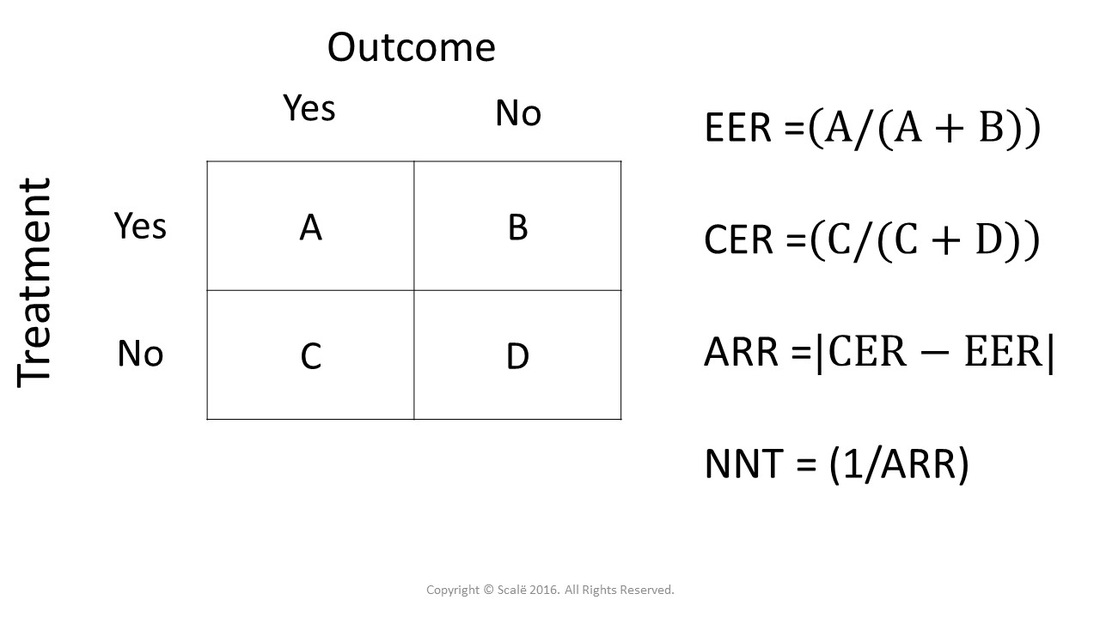
Number Needed to Treat
How many people have to be treated to prevent a future bad outcome?
Number Needed to Treat (NNT) tells clinicians how many people you have to treat to prevent a bad outcome. The formula for number needed to treat is (1/ARR). As the absolute risk reduction increases, the number needed to treat will decrease, meaning that the treatment is more efficacious.
Clinicians ultimately want number needed to treat to be LOW, meaning that few people need to be treated to prevent a bad outcome. As the absolute risk reduction decreases, denoting a small treatment effect, the number needed to treat will increase and more people will have to be treated to prevent a bad outcome.
Clinicians ultimately want number needed to treat to be LOW, meaning that few people need to be treated to prevent a bad outcome. As the absolute risk reduction decreases, denoting a small treatment effect, the number needed to treat will increase and more people will have to be treated to prevent a bad outcome.
Number Needed to Treat (NNT)
Click on the Download Database button for a database structured for epidemiological data. Click on the Download Calculator button to download a free epidemiological calculator.
Hire A Statistician
DO YOU NEED TO HIRE A STATISTICIAN?
Eric Heidel, Ph.D., PStat will provide you with statistical consultation services for your research project at $100/hour. Secure checkout is available with Stripe, Venmo, Zelle, or PayPal.
- Statistical Analysis on any kind of project
- Dissertation and Thesis Projects
- DNP Capstone Projects
- Clinical Trials
- Analysis of Survey Data